1 月 . 17, 2025 05:00
Back to list
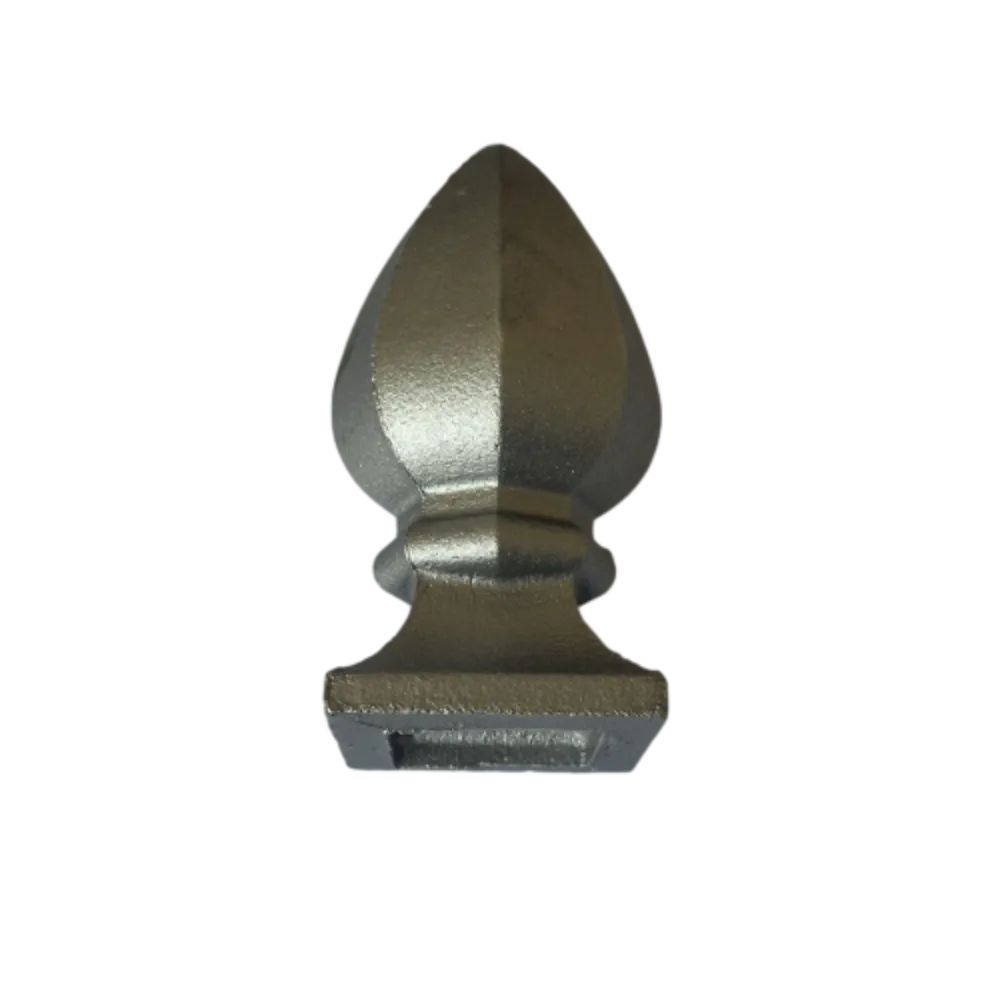
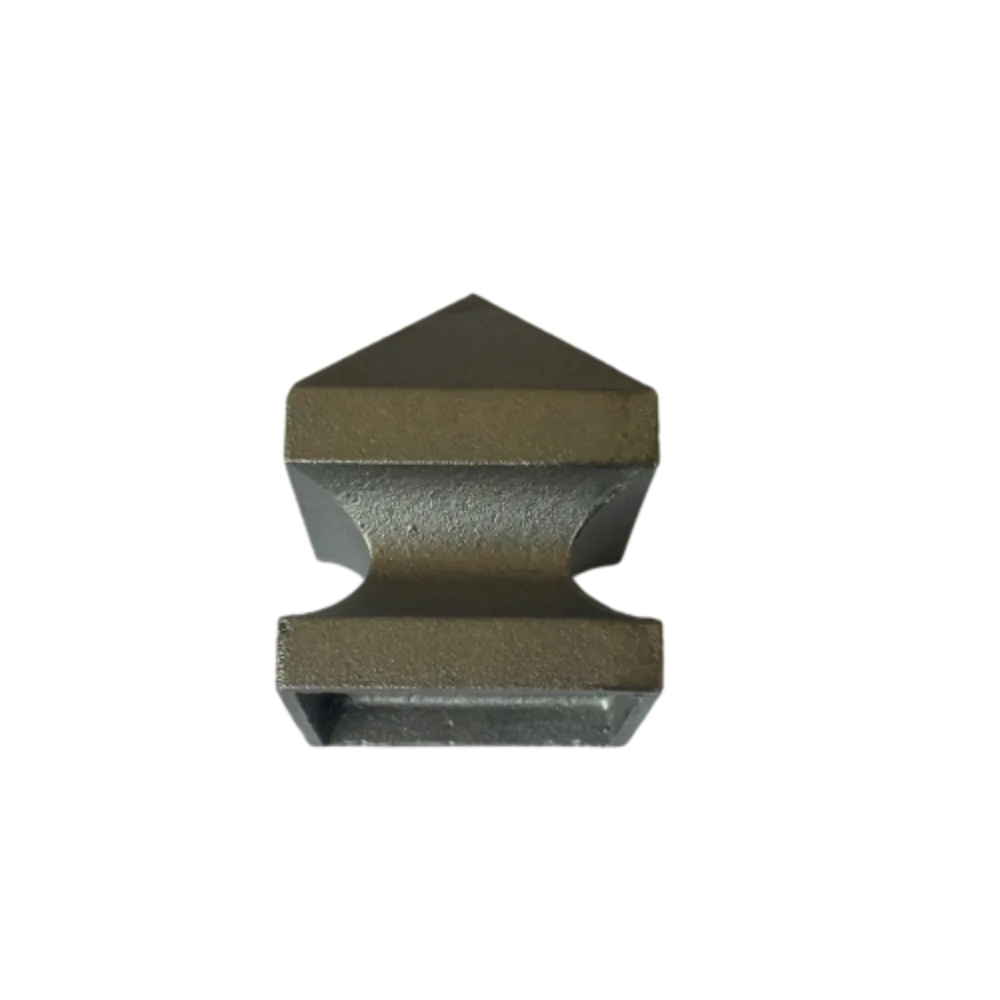
Cast Iron Post Caps
Cast iron collars have emerged as an indispensable component in a wide range of industrial applications, offering an exemplary blend of durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Recognized for their unparalleled strength and resilience under harsh conditions, these collars are often the first choice for securing and supporting pipes, rods, and various cylindrical objects.
In practical applications, the trustworthiness of cast iron collars manifests through their adaptability. Available in a variety of sizes and configurations, they can be tailored to meet specific operational needs. For example, split-collar designs enable easy installation and adjustment without dismantling existing assemblies, which can save significant time during maintenance procedures. This adaptability not only ensures operational efficiency but also enhances safety, as securely fitted collars are less likely to give way, decreasing the likelihood of accidents. The extensive use of cast iron collars in infrastructure projects further underscores their indispensability. For example, in plumbing, these collars are used to join sections of pipes firmly, ensuring no leaks occur in water or gas lines. Similarly, in mechanical systems, they hold shafts and axles in place, maintaining alignment and reducing wear on components. A testament to the educational depth surrounding cast iron collars is provided by detailed case studies and technical manuals that delve into their application across varied industrial contexts. Such resources offer valuable insights into optimal use cases, installation techniques, and maintenance best practices, serving as a rich source of information for engineers and technicians striving to augment their knowledge and application skills. In conclusion, cast iron collars stand as an archetype of industrial excellence, balancing durability, versatility, and economic viability in a way that few materials can match. They represent a strategic investment in quality and reliability, backed by decades of industry experience and expertise. Their continued use in critical applications affirms their relevance and underscores their role as a reliable component in supporting the infrastructure of innovation and industry.

In practical applications, the trustworthiness of cast iron collars manifests through their adaptability. Available in a variety of sizes and configurations, they can be tailored to meet specific operational needs. For example, split-collar designs enable easy installation and adjustment without dismantling existing assemblies, which can save significant time during maintenance procedures. This adaptability not only ensures operational efficiency but also enhances safety, as securely fitted collars are less likely to give way, decreasing the likelihood of accidents. The extensive use of cast iron collars in infrastructure projects further underscores their indispensability. For example, in plumbing, these collars are used to join sections of pipes firmly, ensuring no leaks occur in water or gas lines. Similarly, in mechanical systems, they hold shafts and axles in place, maintaining alignment and reducing wear on components. A testament to the educational depth surrounding cast iron collars is provided by detailed case studies and technical manuals that delve into their application across varied industrial contexts. Such resources offer valuable insights into optimal use cases, installation techniques, and maintenance best practices, serving as a rich source of information for engineers and technicians striving to augment their knowledge and application skills. In conclusion, cast iron collars stand as an archetype of industrial excellence, balancing durability, versatility, and economic viability in a way that few materials can match. They represent a strategic investment in quality and reliability, backed by decades of industry experience and expertise. Their continued use in critical applications affirms their relevance and underscores their role as a reliable component in supporting the infrastructure of innovation and industry.
Next:
Latest news
-
Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?NewsOct.28,2024
-
The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your KitchenNewsOct.28,2024
-
Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and FeaturesNewsOct.28,2024
-
Innovations in Cast Iron Panel TechnologyNewsOct.28,2024
-
The Benefits of Customizing Your Wrought Iron Fence PartsNewsOct.28,2024
-
The Immortal Legacy of Cast Iron Spears: From War to Decorative UseNewsOct.21,2024
-
 Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?Oct-28-2024Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?
Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?Oct-28-2024Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer? -
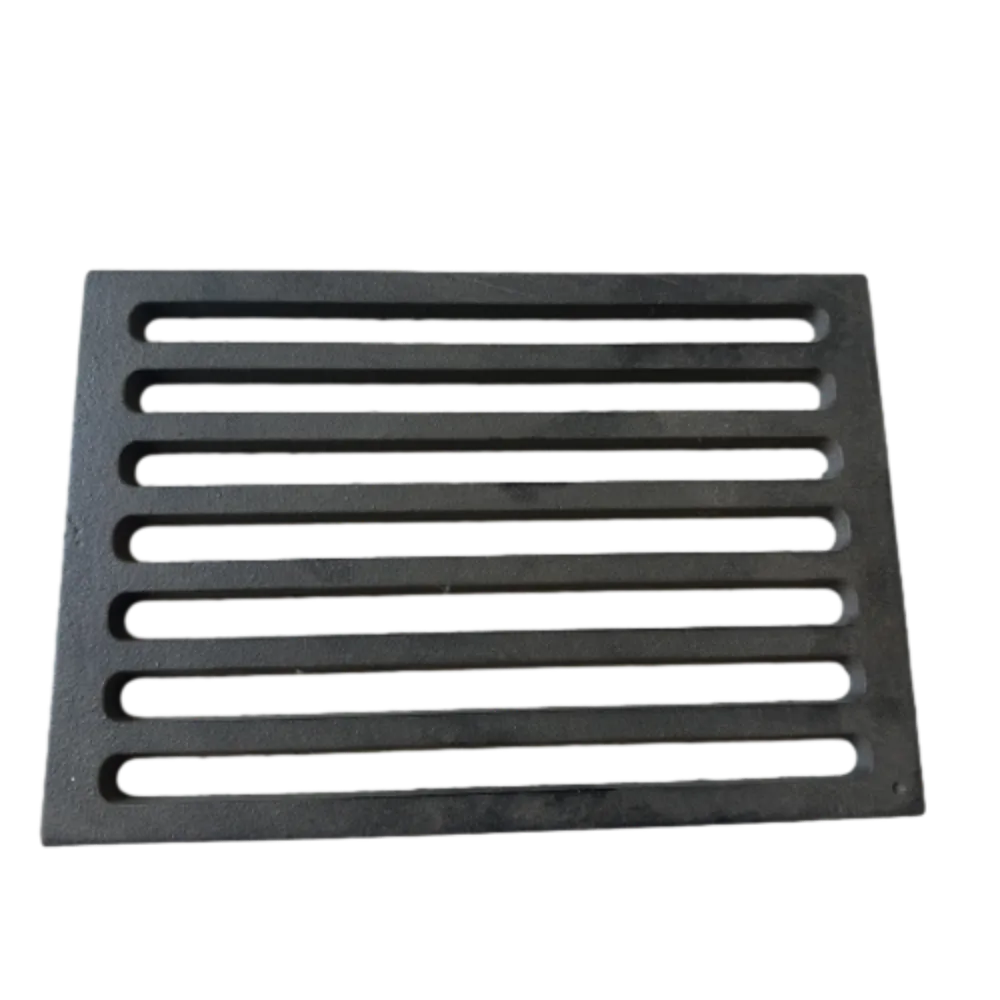 The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your KitchenOct-28-2024The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your Kitchen
The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your KitchenOct-28-2024The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your Kitchen -
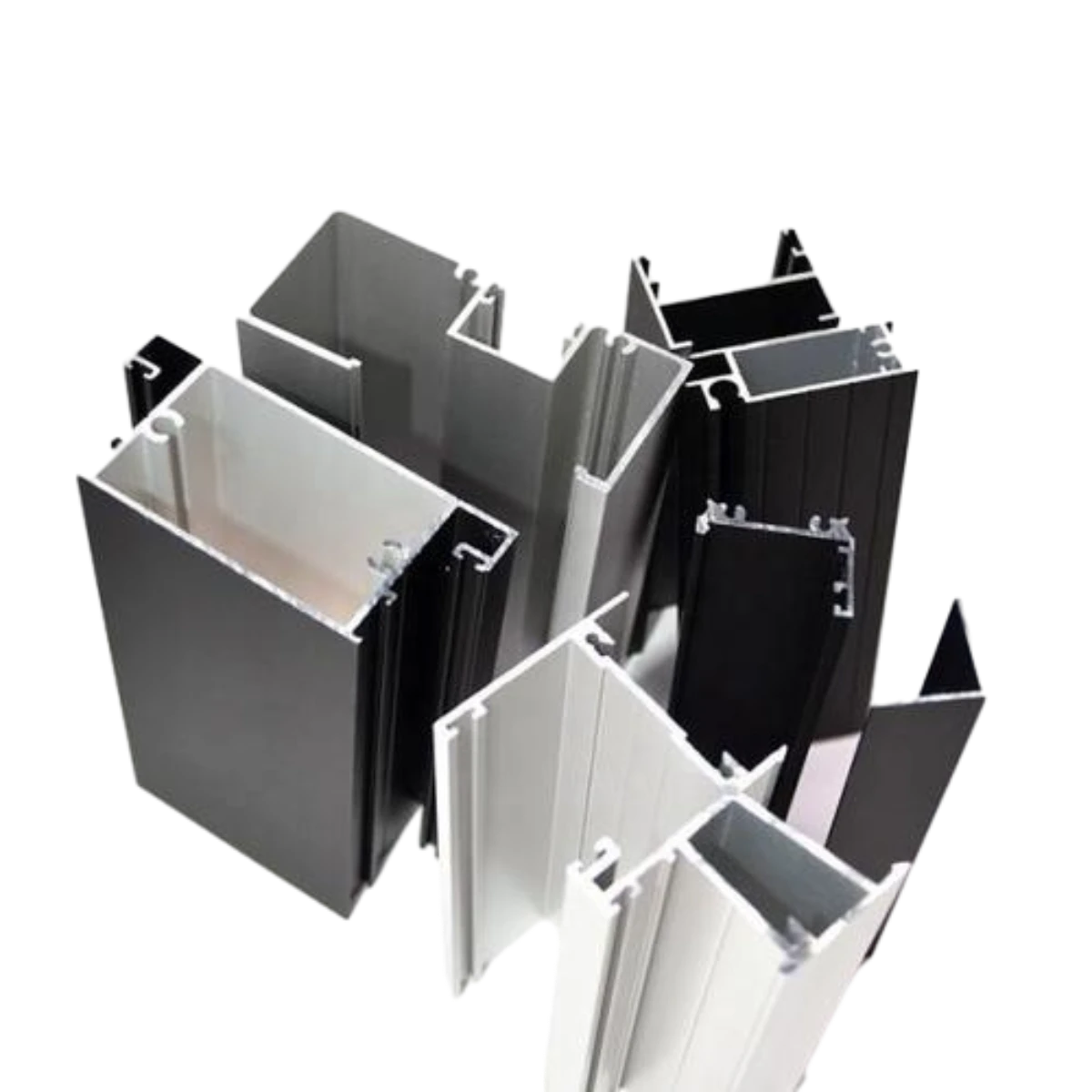 Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and FeaturesOct-28-2024Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and Features
Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and FeaturesOct-28-2024Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and Features