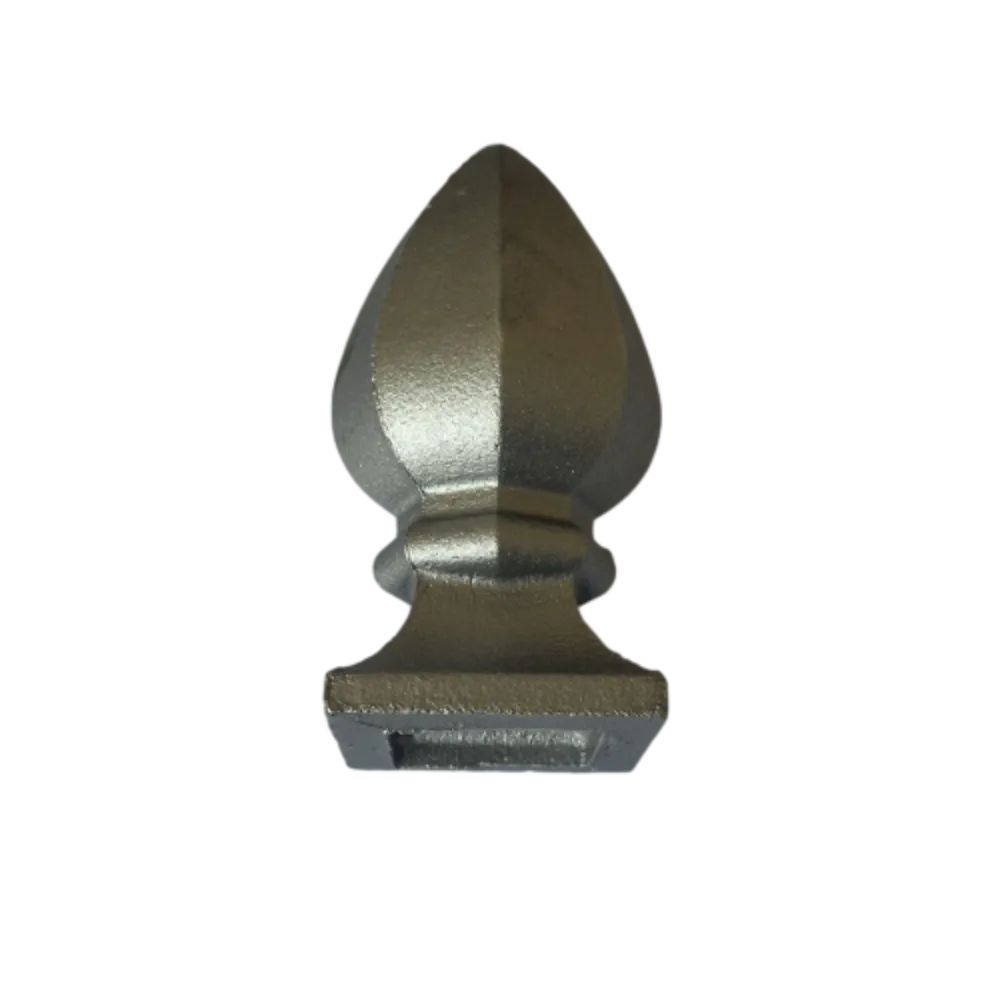
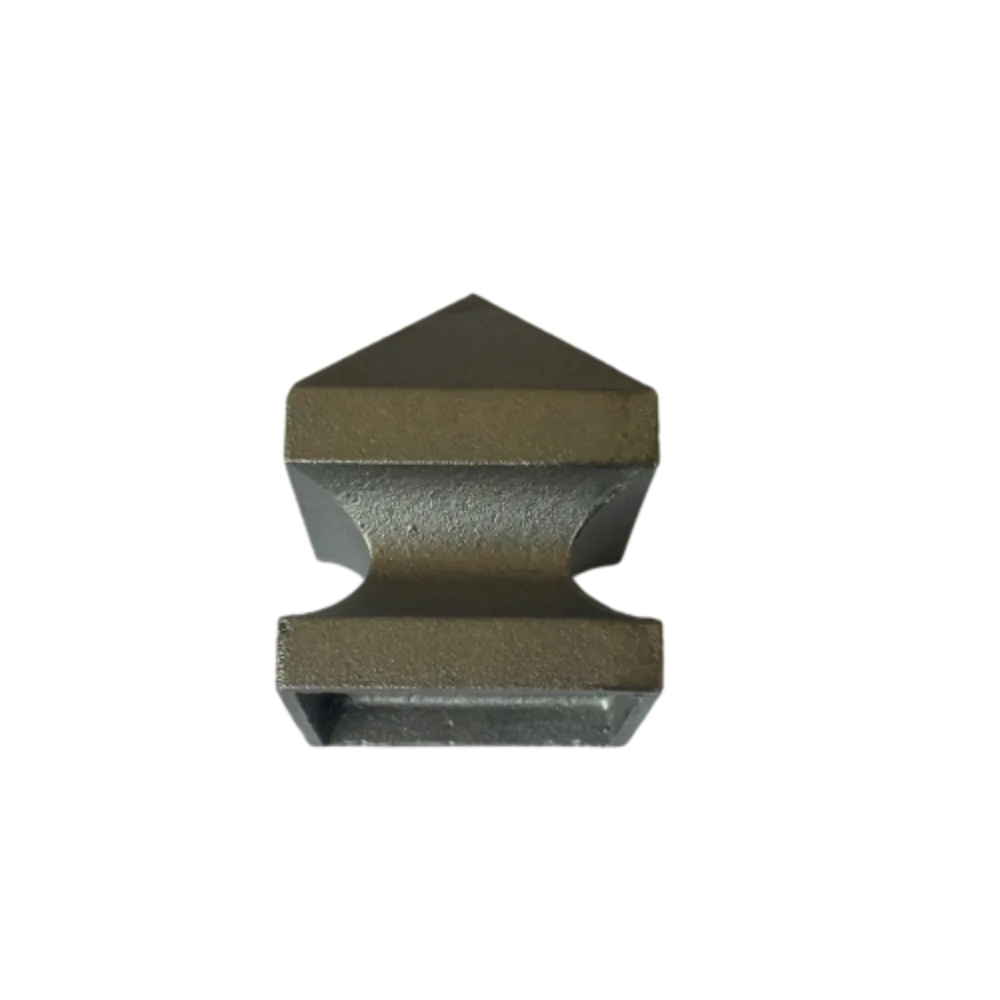
Recrafted Spear Point for Enhanced Performance and Durability
The Forged Spearhead Craftsmanship and Legacy
Throughout history, the spear has served as one of humanity's most essential tools for hunting, warfare, and ceremonial purposes. Its design has evolved over thousands of years, but one constant has been the spearhead. Among the various methods of crafting spearheads, one of the most notable is the process of forging. The forged spearhead, with its remarkable durability and sharpness, symbolizes not only the ingenuity of early human craftsmanship but also the lasting impact of such weaponry on culture and society.
The Craft of Forging
Forging is an ancient technique that involves shaping metal using localized compressive forces, often delivered by hammering. This method enhances the strength and resilience of the metal, making forged spearheads not only more reliable in combat but also more effective in hunting. The process starts with heating the metal, often iron or steel, until it becomes malleable. Craftsmen (or blacksmiths) would then hammer the metal into shape, sharpening the tip and refining the edges.
One of the greatest advantages of forged spearheads is their ability to withstand stress. Unlike cast metal, which can be brittle and prone to breaking under pressure, forged spearheads benefit from the continuous structure formed during the hammering process. The fibers of the metal align in such a way that they enhance the spearhead’s durability, allowing it to penetrate targets more effectively.
Historical Significance
The significance of the forged spearhead stretches far beyond its practical applications. In many ancient cultures, the spear was not merely a tool for survival; it was also a symbol of power and prestige. Warriors often personalized their spearheads, decorating them with engravings or embellishments that represented their lineage or achievements in battle. The skill involved in crafting a spearhead became a mark of respect, with master blacksmiths gaining status within their communities.
forged spear head

Throughout different civilizations, the forged spearhead played a pivotal role in warfare strategies. In ancient Rome, for instance, the pilum was a heavy type of thrown spear used by soldiers, its forged head designed to bend upon impact, preventing enemies from throwing it back. The design of the forged spearhead influenced military tactics; a well-crafted spear could turn the tide of battle, allowing smaller forces to hold their ground against larger armies.
Technological Evolution
As time progressed, the methods of crafting spearheads evolved. The introduction of advanced metallurgy and techniques allowed for greater versatility in design. The crafting of spearheads transitioned from solely forging to include techniques such as casting, welding, and even modern manufacturing processes. However, the timeless appeal of the forged spearhead remains strong, as contemporary blacksmiths and artisans appreciate the artistry involved in traditional methods.
In modern times, the forged spearhead has also found popularity among historical reenactors and collectors. Many enthusiasts value the craftsmanship and historical significance of these artifacts, with authentic replicas being produced to honor ancient techniques. The resurgence of interest in traditional blacksmithing and weapon-making crafts reflects a broader yearning to connect with history and appreciate the skills of our ancestors.
Conclusion
The forged spearhead stands as a testament to the ingenuity and resourcefulness of early human societies. It encapsulates the marriage of function and artistry, serving not only as an effective tool in warfare and hunting but also as a cultural symbol. Through the ages, the forged spearhead has influenced military strategies, craftsmanship, and even social status. As we continue to explore and appreciate our historical legacies, the forged spearhead remains a powerful emblem of human creativity, resilience, and the ongoing journey of technological evolution. Whether as an artifact in a museum or a piece in a modern smithy, the forged spearhead tells stories that span generations, connecting us to the past while inspiring future craftsmen.
-
Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?NewsOct.28,2024
-
The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your KitchenNewsOct.28,2024
-
Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and FeaturesNewsOct.28,2024
-
Innovations in Cast Iron Panel TechnologyNewsOct.28,2024
-
The Benefits of Customizing Your Wrought Iron Fence PartsNewsOct.28,2024
-
The Immortal Legacy of Cast Iron Spears: From War to Decorative UseNewsOct.21,2024
-
 Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?Oct-28-2024Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?
Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer?Oct-28-2024Why Choose TJJ as Your Window and Door Hardware Manufacturer? -
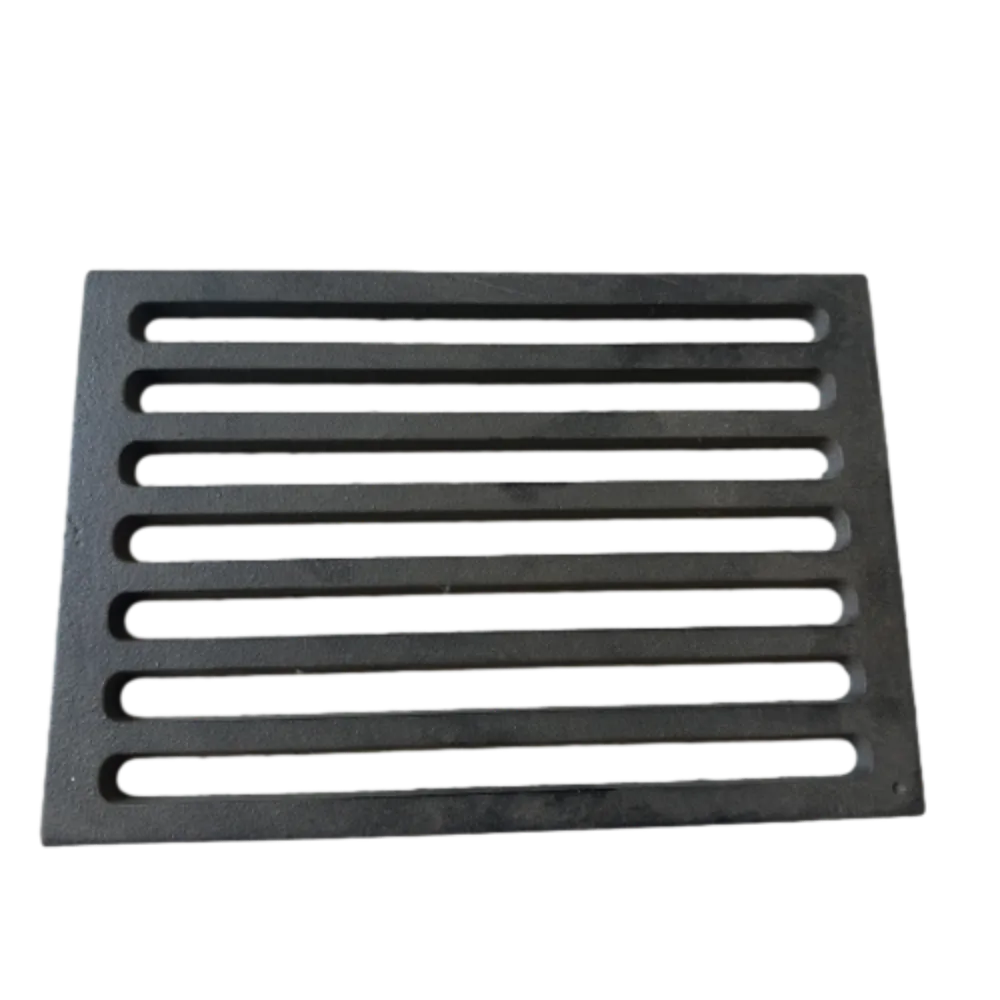 The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your KitchenOct-28-2024The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your Kitchen
The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your KitchenOct-28-2024The Advantages of Cast Iron Stove Plates: A Timeless Choice for Your Kitchen -
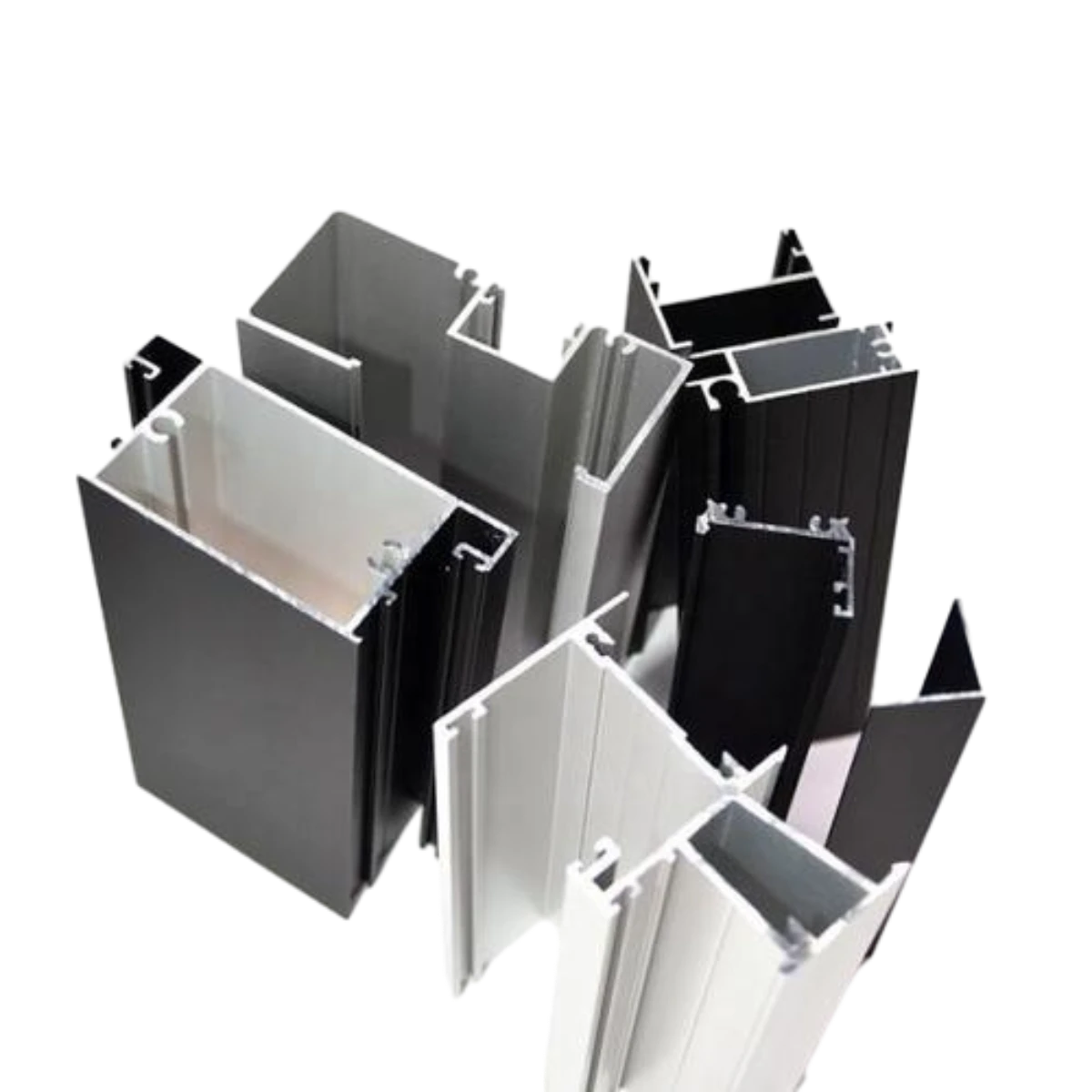 Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and FeaturesOct-28-2024Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and Features
Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and FeaturesOct-28-2024Aluminium Windows Profiles: Benefits and Features